- +86-138 4056 0445,+86-151 4027 2439
- info@careagemedical.com
Product Name: Hydraulic Patient Lift Product Model Number: 71910 Width: 590 mm Push Handle Height: 1140 mm Weight Limited: 150 kg
Product Name: Electric Patient Lift Product Model Number: 71970 Width: 590 mm Push Handle Height: 1140 mm Weight Limited: 150 kg
The electric patient lift which can easily move the patient up and down , saving effort and meeting the life needs of the patient. Transfers may be to and from beds, chairs, floor to bed, lateral transfers, bathing, and toileting , and offers a wide selection slings for a variety of lifting situations.
Guided Reading
In the process of treating patients, the wheelchair is a very widely used tool, such as lower limb disability, hemiplegia, paraplegia below the chest and mobility disabilities are very suitable. As a rehabilitation therapist, it is very necessary to know the characteristics of wheelchair, choose the most suitable wheelchair and the most correct use method.
Do you have a thorough understanding of wheelchair selection and use?
If a patient or family member asks you how to choose and use a wheelchair, can you give a reasonable prescription for a wheelchair?
First of all, what kind of damage can an unsuitable wheelchair do to the user?
Local compression is too great
Bad posture
To induce scoliosis
Causing joint contractures
What are the unsuitable wheelchairs: the seats are too shallow and not high enough; the seats are too wide and not high enough
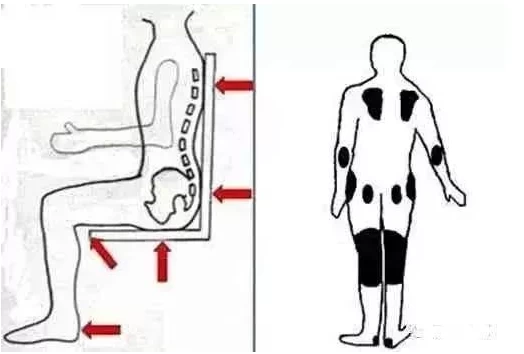
The major stress areas of wheelchair users were the ischium tubercle, thigh, carmine and scapular region. Therefore, in the choice of wheelchair to pay attention to these parts size is appropriate to avoid skin wear, abrasions and pressure sores.
The choice of wheelchair, this is the most basic knowledge of rehabilitation therapists, must be kept in mind!
The choice of a regular wheelchair
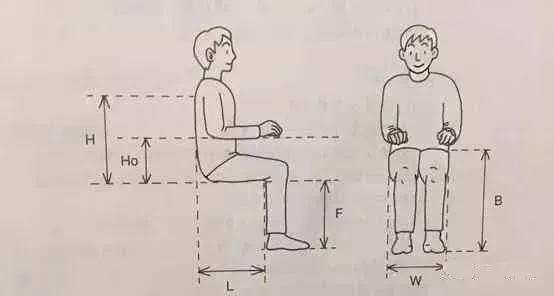
Seat width
Measure the distance between your hips or strands when you sit. Add 5 cm to the distance, leaving 2.5 cm on each side. The seat is too narrow, up and down the wheelchair is more difficult, hip and thigh tissue is compressed; the seat is too wide, not easy to sit down, wheelchair manipulation is not convenient, both upper limbs easy fatigue, in and out of the door is also difficult.
Seat length
The horizontal distance between the buttocks and the calf gastrocnemius muscles was measured after sitting, and the measurement was reduced by 6.5 cm. The seat is too short, the weight mainly falls on the sitting bone, the local easy to be pressed too much; the seat is too long will press the Rouge pit department, affects the local blood circulation, and easy to stimulate the skin of this department, to the thigh is extremely short or the hip knee flexion contracture patient, then uses the short seat is better.
Seat height
Measure the distance from heel (or heel) to carmine when sitting. Add another 4cm and place the pedal at least 5cm off the floor. The seat is too high for the wheelchair to enter the table; the seat is too low for the sitting bones to bear too much weight.
Seat Cushion
For comfort and prevention of pressure sore, seat cushion should be placed, available foam rubber (5 ~ 10cm thick) or gel cushion. A piece of plywood 0.6 cm thick can be placed under the seat cushion to prevent the seat from sinking.
Backrest height
The higher and more stable the backrest, the lower the backrest, the greater the range of motion of the upper body and upper limbs. A low backrest measures the distance from the seat surface to the armpit (one or both arms are stretched forward and flat) , subtracting 10 cm from the result. High back: measure the actual height of the seat from the face to the shoulders or back.
Handrail height
Sit with your upper arm vertical and your forearm flat on the armrest. measure the height of the chair to the lower edge of your forearm, plus 2.5 cm. Proper armrest height helps maintain correct body posture and balance, and allows the upper limbs to be placed in a comfortable position. The armrest is too high, the upper arm is forced up to lift, easy to feel tired. Armrest is too low, need upper body to lean forward to maintain balance, not only easy fatigue, may also affect breathing.
Other accessories for wheelchairs
To meet the special needs of patients and design, such as increased handle friction surface, brake extension, anti-shock Device, anti-skid device, armrest installation, wheelchair table convenient for patients to eat, write and so on.
Points to note when using a wheelchair
Push the wheelchair on the level ground: the old man sits firmly to hold on, treads firmly the pedal. The attendant stands behind the wheelchair and pushes the wheelchair at a slow and steady speed.
Uphill wheelchair: the uphill body must be tilted forward to prevent backflip.
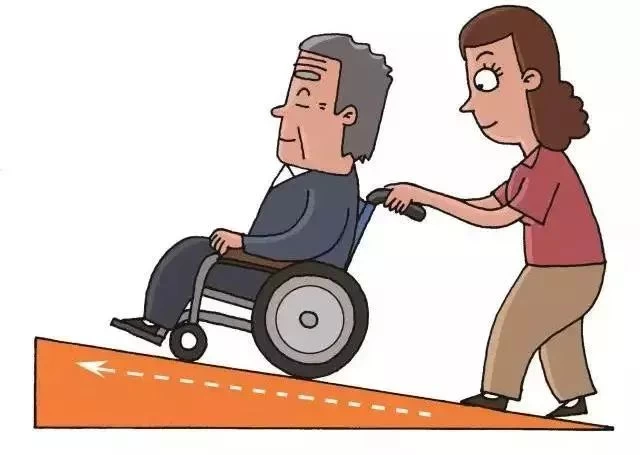

Downhill Backward Wheelchair: Downhill Backward Wheelchair, step back, wheelchair down a bit. Stretch your head and shoulders and lean back. Ask the old man to hold on to the handrail.
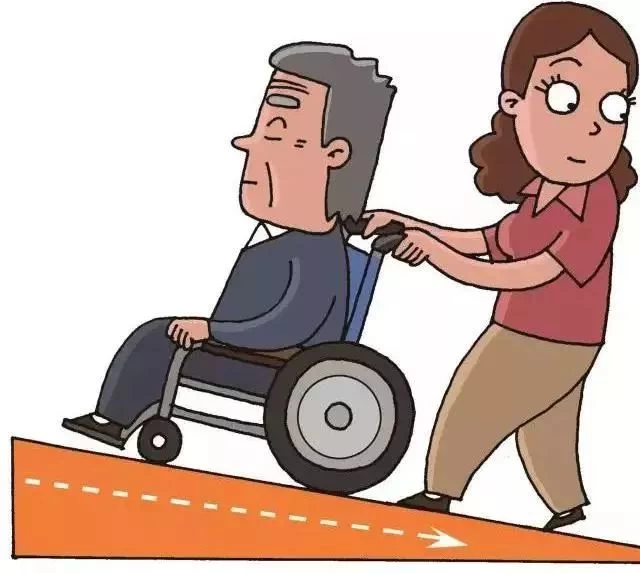

Step Up: Please hold on to the back of the chair with both hands, don’t worry.
Step on the pressure foot power frame to lift the front wheel (to the two rear wheels as a fulcrum, so that the front wheel smoothly moved up the steps) gently placed on the steps. Keep the rear wheel close to the step and lift the rear wheel. Lower the center of gravity by moving the rear wheel closer to the wheelchair.

Rear Foot on power rack
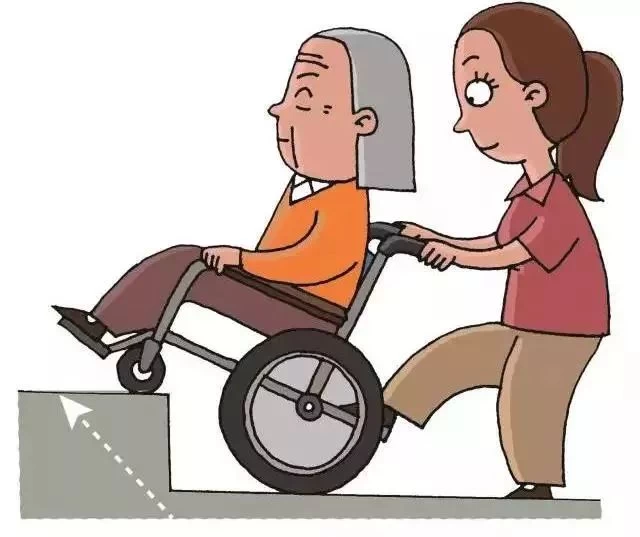

Step Backward Wheelchair: step backward wheelchair, wheelchair slowly down, stretching the head and shoulders and leaning back, told the elderly to hold onto the handrails. Stay close to the chair. Lower your center of gravity.
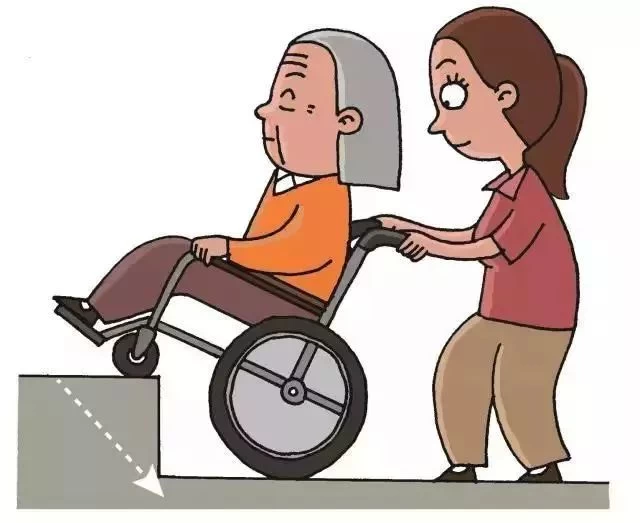
Push the wheelchair up and down the elevator: both the elderly and the caregiver turn their backs toward the direction of the caregiver in front, and the wheelchair pulls the brake as it enters the elevator behind them -- telling the elderly in advance how to enter and exit the elevator through rough terrain.
Wheelchair transfer
Take the vertical transfer of hemiplegic patients as an example
It is suitable for any patient who can maintain stable standing when hemiplegia and standard shift.
(1) transfer of bed to wheelchair
The bed height should be close to the wheelchair seat. A short armrest should be installed at the head of the bed. The wheelchair is provided with a brake and a removable baseboard. The wheelchair is placed on the healthy side of the patient. The wheelchair is 20-30(30-45) degrees from the foot of the bed.
The patient sits next to the bed, first locking the brake of the wheelchair, leaning forward with the torso, and using the legs to help move to the bedside. The healthy limb is flexed to above 90 degrees, and the healthy side foot is moved to the affected side foot later, so as to facilitate the free movement of the two feet.
Hold the armrest of the bed and move the patient’s torso forward, using his or her healthy arm to support him or her forward, so that most of the weight is transferred to the healthy leg to reach the standing position.
The patient moves his or her hand to the middle of the far arm rest of the wheelchair and moves his or her feet into a ready-to-sit position. When the patient is in the wheelchair, adjust his position and release the brake.
Back off, wheelchair, off the bed. Finally, the patient places the foot pedal in the original position, uses the healthy side hand to lift the side leg, and puts the foot on the foot pedal.
(2) wheelchair transfer to bed
The wheelchair is facing the head of the bed, approaching the healthy side, applying the brakes. Lift the affected leg with the healthy hand, move the foot pedal to the side, lean your torso forward and down, and move your face to the front of the wheelchair until your feet are down and your feet are just behind the affected foot.
Grasp the arms of the wheelchair, move your body forward, and support your weight by moving up and down the healthy side to reach the upright position. After standing, move your hands onto the armrest of the bed and slowly rotate your body so that you are ready to sit on the bed, then sit on the bed.
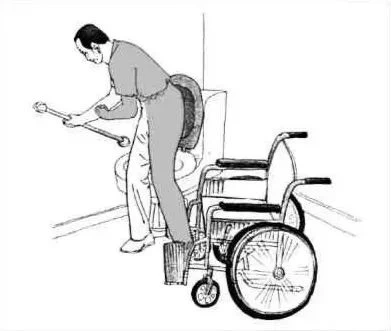
(3) wheelchair transfer to toilet
The chair is placed diagonally so that the healthy side of the patient is close to the toilet, the brake is applied, the foot is removed from the pedal, and the pedal is moved to the side.
Lean your torso forward by pressing your strong hand against the armrest of your wheelchair. Move forward in a wheelchair. Use your healthy side legs to support most of your weight as you stand up from your wheelchair.
Stand and rotate your feet. Until You’re standing in front of the toilet. The patient pulled down his pants and sat down on the toilet. Transfer from the toilet to the wheelchair can be carried out in reverse according to the above procedures.
In addition, there are many kinds of wheelchairs on the market, which can be divided into aluminum alloy, light material and steel, such as ordinary wheelchairs and special wheelchairs.
Special wheelchair can be divided into: Leisure Sport Wheelchair series, electronic wheelchair series, seat side wheelchair series, help station wheelchair series. Here’s a look at the range of wheelchairs available.
1. A regular wheelchair
The utility model is mainly composed of a wheelchair frame, a wheel, a brake and other devices

Scope of application: lower limb disability, hemiplegia, paraplegia below the chest and mobility of the elderly.
Features:
1. The patient can operate the fixed handrail or detachable handrail by himself
2. Stationary or removable foot pedals
3. Fold when carrying or not in use
2 high backrest reclining wheelchair

Scope of application: high paraplegia and senile frail patients
Features:
1. The backrest of the reclining wheelchair is as high as the detachable armrest of the head and the swivel pedal. The pedal can be lifted and lowered to rotate 90 degrees, and the bracket can be adjusted to a horizontal position.
2. The backrest can be adjusted in segments or can be adjusted arbitrarily to the level (equivalent to a bed) . The user can rest in a wheelchair. The headrest can also be removed.
3 electric wheelchairs
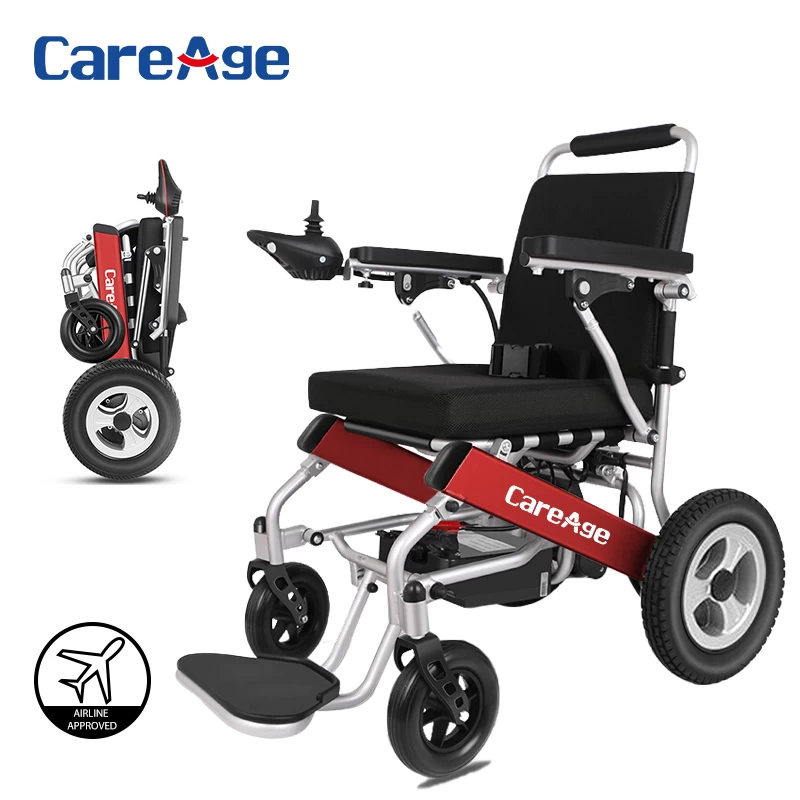

Scope of application: for high paraplegia or hemiplegia, but one-handed control of the use of people
Features: electric wheelchair powered by batteries, a charge capacity of about 20 km, one-handed control device, can forward, backward and turn, can be used in indoor and outdoor. Higher prices.
4 toilet chairs
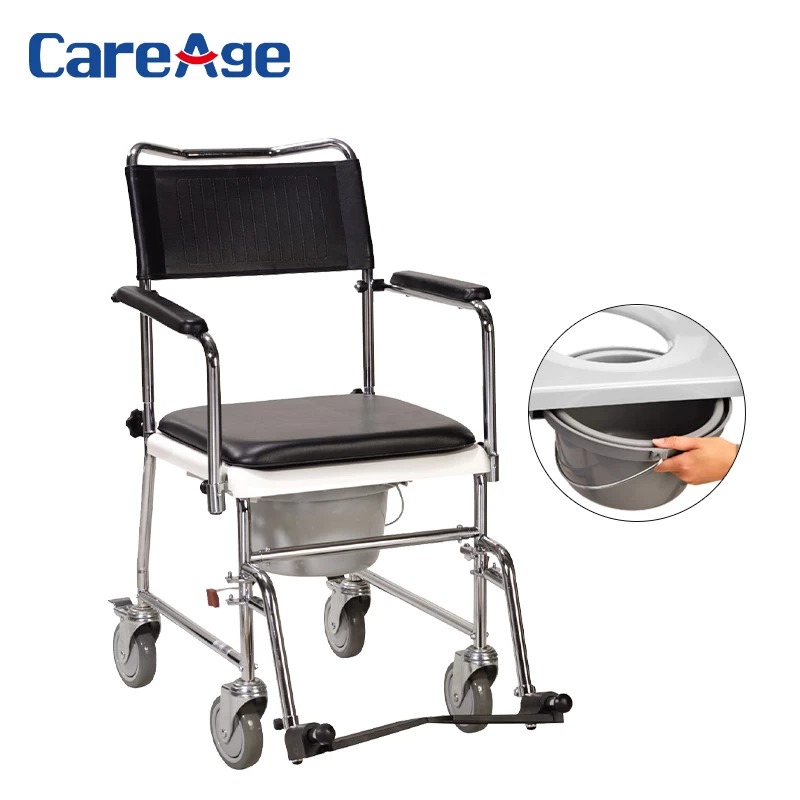

Scope of application: for the disabled and the elderly who can not go to the toilet by themselves.
Features: divided into small wheel chair, toilet bucket wheelchair, can be used according to the occasion of choice.
5 exercise wheelchairs

Scope of application: for disabled people in sports activities, divided into ball games and racing two categories.
Features: special design, the use of materials generally used aluminum alloy or light-weight materials, strong and lightweight.
6. Station wheelchair
Its a standing, dual-use wheelchair

Scope of application: for paraplegia or cerebral palsy patients to stand training.
Features:
One is to prevent osteoporosis in patients, promote blood circulation and strengthen muscle strength training.
Second, it is convenient for patients to take things. Scope of application: paraplegia, Cerebral Palsy patients.